From light bulbs to lipstick, coffeemakers to clothes, the products we use on a daily basis are subject to standards. These standards help keep us safe and help businesses compete in an ever-expanding global economy.
ANSI standards cover everything from safety for employees and consumers to manufacturing processes to product distribution. In this guide, we’ll explore why ANSI exists and what role it plays in the development of standards adopted throughout the US.
What is the American National Standards Institute (ANSI)?
ANSI is a private, not-for-profit group that supports voluntary standards and conformity assessment systems that apply to products, processes, services, systems, and personnel. According to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), standards are “documents established by consensus that provide rules, guidelines or characteristics or their results.”
ANSI does not develop American National Standards but instead offers the ideal environment for them to be created by standard development organizations. ANSI monitors the standardization process and accredits Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs), which are public or private entities responsible for creating American National Standards.
The organization also helps create the assessment processes that SDOs use when developing standards. ANSI’s work has created a fair and diplomatic way for any interested parties to take part in standards creation.
Some SDOs accredited by ANSI include ASTM International, Underwriters Laboratories, Inc., NFPA International, ASME International, ASHRAE, CSA America, Inc., and NSF International.
The over 1,000 members of ANSI represent more than 270,000 companies, professional societies, trade associations, government agencies, and consumer and labor organizations. ANSI lobbies for over 30 million professionals and covers nearly every industry across the globe. ANSI standards not only protect and promote businesses, but they also ensure public safety and support the economy.
A Brief History of ANSI
Founded in 1918, the organization has had a long, storied history in the United States. It began when five engineering societies and three government agencies joined together to support U.S. businesses and industries.
After undergoing several name changes throughout the years, ANSI adopted its current name in 1969.
Currently, ANSI is headquartered in Washington, D.C. with an operations office in New York City. It is led by a Board of Directors and a management team and employs 90 workers.
ANSI’s Role in Voluntary Standards
With national, state and local government standards already in place, why would a company choose to join ANSI and work with voluntary standards?
Because membership and participation are completely voluntary, all ANSI’s members have extra skin in the game and are dedicated to building their businesses and helping the economy. This is done through the creation of voluntary standards, called American National Standards.
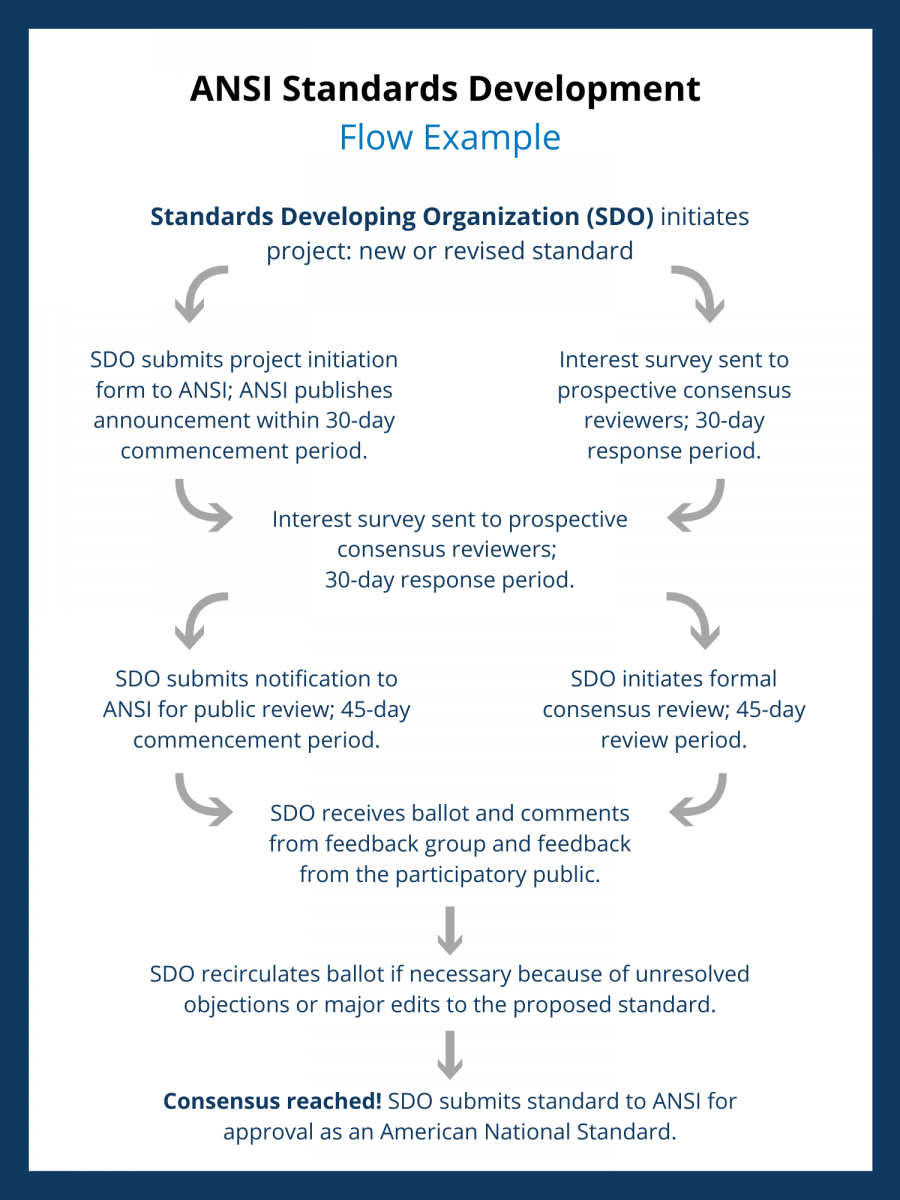
ANSI’s accreditation of Standard Development Organizations (SDOs) assures that each one maintains levels of openness, balance, consensus, and due process.
As of January 2018, the United States has 237 ANSI-accredited SDOs and over 11,500 American National Standards. The 20 largest SDOs are responsible for over 90 percent of all voluntary standards.
All American National Standards are considered “open” standards. They are developed in such a way that all interested and affected parties are given a chance to be a part of their creation. The standard development process is collaborative, balanced and uses a consensus-based approval process.
Because ANSI is the only accreditor of voluntary SDOs in the United States, businesses and consumers are reassured that the standards developed by SDOs with ANSI accreditation meet rigorous requirements. Having these standards in place allows those businesses to bring new products and services to consumers and compete locally and globally.
The creation of just one standard consists of hours of data gathering and discussion of viewpoints and the input from numerous subject matter experts. As the marketplace changes and evolves, so do standards. They are flexible so they can easily change and adapt as the market changes.
The Importance of Standards Development
We see standards at work in every part of our everyday lives. Standards set the size, shape or capacity of a product, process or system. They lay out the performance duties of a product or personnel.
A standard also defines terms so the interpretation of the standard is clear to all using it. For example, because of standards, all electronics and appliances can be plugged into the same type of outlets.
Standards are key to a successful economy because they provide a way for consumers to evaluate a product or service. Standards allow companies to provide quality goods and products and fairly compete in the national and international markets. Consumers and products are safer thanks to standards.
The voluntary nature of these standards does not mean they don’t have to be followed. It refers to the process of their creation and implementation.

ANSI and Government Affairs
To help protect voluntary standards, ANSI stays highly involved in government affairs. The main function of ANSI in government affairs is an information provider, acting as a liaison between standard developers and government agencies that are making policy that directly affects their efforts.
Because it is not a government agency, ANSI cannot help with consumer complaints with a product or service, even those that comply with an American National Standard.
ANSI constantly champions for government agencies using voluntary standards developed in the private section along with government-created standards. Public policy outreach programs from ANSI inform and educate legislators, especially those dealing with trade and commerce issues, on the importance of private sector standards.
The federal government plays a cooperative role in ANSI activities, working with the organization to protect company interests, protect consumers and encourage a strong economy. A number of U.S. government agencies have representatives that take part in ANSI activities.
In 1996, Congress passed the National Technology Transfer and Advancement Act. This law requires federal agencies to utilize voluntary standards when applicable and participate in conformity assessment systems. Since then, the number of federal agencies using voluntary standards has doubled, according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Conformity Assessment
Standards are useless until they are implemented correctly. ANSI champions for conformity assessment, which is the process in which a product, process, system, service or personnel fulfills the requirements of a specific standard. Conformity assessment proves that a product meets a standard for safe and effective use. It gives consumers, buyers, sellers, regulators and producers confidence in a product.
Conformity assessment is completed through:
- Sampling
- Testing
- Inspection
- Certifications
- Management system assessment and registration
ANSI offers accreditation to organizations that perform conformity assessments. The ISO/IEC offers a series of standards (17000) that act as a guide to conformity assessment. These standards explain conformity assessment for both those being assessed and those doing the assessing.
ANSI’s Role in International Standards
The United States has its own set of voluntary standards used in the country. Many international standards also exist that affect the way American companies can do business.
ANSI serves as the U.S. representative to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), representing the interests of U.S. companies and businesses. Via the U.S. National Committee, it is also the U.S. representative to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
The ISO works across the globe to develop, coordinate and promote international standards. IEC is another world-wide organization that prepares and publishes international standards in the electrical and electronic spheres.
Promoting the use of U.S. standards internationally, ANSI advocates for U.S. businesses and policies. It works to encourage the ISO and IEC to adopt U.S. standards on the international scene.
The ANSI Accreditation Board is also a member of:
- International Accreditation Forum
- International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation
- Asia Pacific Accreditation Cooperation
- InterAmerican Accreditation Cooperation
Consumer Standards
Consumers demand safe and effective products. ANSI’s Consumer Affairs department provides information to consumers on the over 100,000 standards currently in action in the United States. It acts as a liaison between standard developers and consumer groups so that developers take consumers’ interests in mind when creating standards.
ANSI makes sure that consumers have a say in standards creation. Consumers provide valuable information about product use that developers use in creating standards. The ANSI Consumer Forum plays a large role in involving consumers in the standards creation process.
The public can see all proposals for new standards in ANSI’s weekly publication, Standards Action. The publication also lists all proposed revisions, reaffirmations, and withdrawals of existing standards.
Examples of Consumer Standards Developed Through ANSI
Designers and manufacturers of consumer goods can purchase ANSI standards from the ANSI store or through a standards publisher, like IEC.
ANSI consumer standards address a wide variety of consumer goods, packaging, and infrastructure, including:
- Plastics
- Electronic Communication
- Road Vehicles
- Medical Devices
- Identity Protection
- Societal Security
- Radio and Telecommunications (Frequency and Disturbance)
- Personal Protective Equipment
The standards for a given topic may cover the engineering of a product, but they often stipulate how best to manage a given product in the field as well.
Safety Standards
One of the most important functions of voluntary standards is safety. The applications are broad, covering consumer and worker safety, engineering and managerial best practices.
Within the collection of American National Standards are a number of safety standards. These safety standards speak directly to the safety of machinery, equipment, personnel and end products. Like with other standards, ANSI doesn’t develop these standards, but rather sets the criteria that developers use to create the standards and accredits those developers.
The United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides mandatory safety regulations that companies and businesses must follow. ANSI encourages companies to utilize voluntary safety standards along with OSHA regulations. Applying both types of standards leads to fewer injuries and deaths and an overall better workplace environment.
ANSI standards publishers include organizations like the American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP), Accredited Standards Committee (ASC), and International Safety Equipment Association (ISEA).
Most safety-related voluntary standards were created in conjunction with ANSI and one of these organizations. Safety standards are then published by the accredited organization.

Examples of ANSI Safety Standards
Companies and organizations can purchase all ANSI standards, including safety standards, through the ANSI web store. Safety standards are available for purchase individually and many are also included in standards packages.
ANSI safety standards fall into a number of broad categories:
- Construction Safety
- Ladder and Lift Safety
- Fall Protection Safety
- Clothing and Equipment Safety
- Workplace Surfaces Safety
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Lockout/Tagout Safety
- Safety Training Development and Delivery
Each of these categories has a number of specific standards. For example, ladder safety includes wooden ladder safety standards, metal ladder safety standards, and safety requirements for mobile ladder stands.
ANSI and ASSP
The American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP) is a professional association that exists to “provide education, standards development, advocacy and a professional community to support the advancement of our members and the profession as a whole.”
Accredited by ANSI, the ASSP is a leader in developing voluntary consensus standards — standards that do beyond OSHA requirements. ASSP develops its standards with the help and oversight of ANSI.
ANSI/ASSP standards address some of the most pressing issues in worker safety, such as machine guarding, lockout/tagout, safety training development and delivery, and safety management.
ANSI works with Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs) to identify the need for a standard, make a plan for the creation of that standard, and invite all stakeholders to participate in the process.
Joining ANSI
Companies, organizations and entities involved in standards and their development can become a member of ANSI and take advantage of a number of benefits. Membership in ANSI also provides networking opportunities and the ability to have a say in standards policies in the United States.
Membership Benefits
The cost of joining ANSI doesn’t come without the benefits to justify it. ANSI helps members network within their industry and across other industries.
Members have access to membership forums in each membership category where they can share ideas, ask and answer questions and collaborate on projects.
ANSI has forums for company, government, organizational and consumer interest members. These forums:
- Provide networking in different categories
- Open up discussions on trends
- Address issues
- Help recruit and retain for ANSI membership
- Allow organizations to represent their interests
Members can also join policy advocacy groups and lobby for different standards-related causes. ANSI advisory groups and committees include the National Policy Advisory Group, Intellectual Property Rights Policy Advisory Group, and the International Policy Advisory Group.
Another way for a member to get involved in policy is through ANSI’s committees and standards panels. These cover a variety of topics and interests and include:
- Appeals Board
- ANSI ISO Council (AIC)
- Board of Standards Review (BSR)
- Executive Standards Council (ExSC)
- United States National Committee (USNC) IEC Council
- Committee on Education (COE)
- International Conformity Assessment Committee (ICAC)
- ANSI ISO Forum (AIF)
- Regional Standing Committees (RSC)
- Technical Management Committee (TMC) of the USNC
- ANSI Unmanned Aircraft Systems Standardization Collaborative (UASSC)
- America Makes & ANSI Additive Manufacturing Standardization Collaborative (AMSC)
- Energy Efficiency Standardization Coordination Collaborative (EESCC)
- Homeland Defense and Security Standardization Collaborative (HDSSC, formerly HSSP)
- ANSI Nanotechnology Standards Panel (ANSI-NSP)
- ANSI Network on Chemical Regulation
ANSI members receive exclusive discounts on standards. Members can save up to 20 percent on standards subscriptions and stand-alone standards. Other discounts include:
- Online masters courses
- ANSI training events
- 10% off on public training for full members
- Reciprocal membership with the Society for Standards Professionals
- Complimentary admission to World Standards Week events
- Up to 50% on shipping and services with UPS
- And others
Additional benefits include:
- Access to panels and workshops
- Active in creating American National Standards
- Legitimacy for belonging to a prestigious standards organization
- Full use of the ANSI member icon
- Access to print and electronic advertising in ANSI publications
Membership Categories
Membership in ANSI is organized into five categories to fit all kinds of types of entities:
Company: This includes any corporations, partnerships or other business entities formed under the laws of the United States that take part in industrial or commercial business. Affiliates, divisions and joint ventures of these companies may also qualify for membership in this category.
International: If a business or organization does not have legal standing in the United States, it would be considered an international member. International members have no voting rights within ANSI.
Organizational: Entities in this category include not-for-profit scientific, technical, professional, labor, consumer or trade organizations involved in standards-related activities.
Government: This includes departments, authorities, and agencies under the national, state, regional or local governments in the United States.
Educational: Any domestic educational institution dealing with standards or conformity assessment.
You can look up any members of ANSI via their website. The search function allows you to lookup by membership category, business name, or organization name.
How to Join
Any organization interested in membership can find the application online. International applicants should use this application. If the organization needs additional information before joining ANSI, it can take part in one of the free webinars that take place on the first Friday of each month. These 30-minute webinars explain the benefits of ANSI membership and ANSI activities.
Once an organization becomes a member, it must pay the yearly dues, charged on a sliding scale depending on the organization’s yearly sales revenue.
Along with yearly dues, members pay an Activity Assessment Fee based on the number of standards they hold. This fee helps defray overall costs and covers the costs for mandatory audits.
Instead of an Activity Assessment Fee, international members pay either a Secretariat Assessment Fee or a “P” Memberships Assessment Fee. The type of assessment they pay depends on the type of standards they hold and whether they administer U.S. Technical Advisory Groups (TAGs).
ANSI Accreditation
ANSI does not create the standards, but instead accredits the organizations that do create standards. They provide support for these SDOs in the form of effective procedures and management services that save the organization time and money.
Working with SDOs, ANSI works to identify needs for a standard, makes a plan for the creation of that standard and allows all stakeholders to participate in the process.
When determining whether a standards-developing organization qualifies for ANSI accreditation, ANSI uses Essential Guidelines, described in more detail below. The process of accreditation starts with applying using the online Application for Accreditation as a Developer of American National Standards.
ANSI charges a one-time application fee of $5,000, which an applicant should submit with the application and a copy of their proposed operating procedures.
ANSI Essential Requirements
Any SDO who wants to obtain ANSI accreditation or maintain it must meet ANSI Essential Requirements. All of the requirements are laid out in ANSI Essential Requirements: Due process requirements for American National Standards. To aid organizations in interpreting the extensive documents, ANSI has published a series of guidance documents.
The main pillars of the requirements are:
- Openness
- Lack of dominance
- Balance
- Coordination and harmonization
- Notification of standards development
- Consideration of views and objections
- Consensus vote
- Appeal
- Written procedures
- Compliance with American National Standards policies
The Essential Requirements set a fair playing ground for standards creation by requiring all SDOs to follow the same procedures. In the spirit of transparency, any time that ANSI makes changes to its Essential Requirements documents, organizations can submit an appeal to those changes. Any proposed changes are published in a weekly newsletter accessible to members and the public.
A similar process governs how a standard becomes an American National Standard. When creating a standard, SDOs must make sure the process includes consensus from all interested parties and public review of the standard draft. Response to the public review comments and incorporating approved changes follows. If needed, anyone who believes the standard doesn’t meet the necessary requirements can follow the appeals process.
Summary
Throughout its long history, ANSI has also acted as a central source of information regarding standards. Its website has an impressive resource section with a news section, annual reports, documents of interest, published articles and an extensive library of speeches and presentations.
ANSI hosts and sends representatives to a wide variety of conferences, symposiums, and workshops around the world. Visit their Meetings and Events page to see a full calendar.
- ANSI Webstore (inventory of standards available for purchase)
- ANSI Incorporated by Reference Portal (library of standard incorporated by U.S. Government)
- What’s New? (biweekly e-newsletter)

